Pre-Shared Key Authentication with EDHOC: The Security-Performance Tradeoff. Elsa Lopez Perez, Thomas Watteyne, Rafael Marin-Lopez, Cristina Onete, Mališa Vučinić. IEEE Access, January 2025. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/11247913
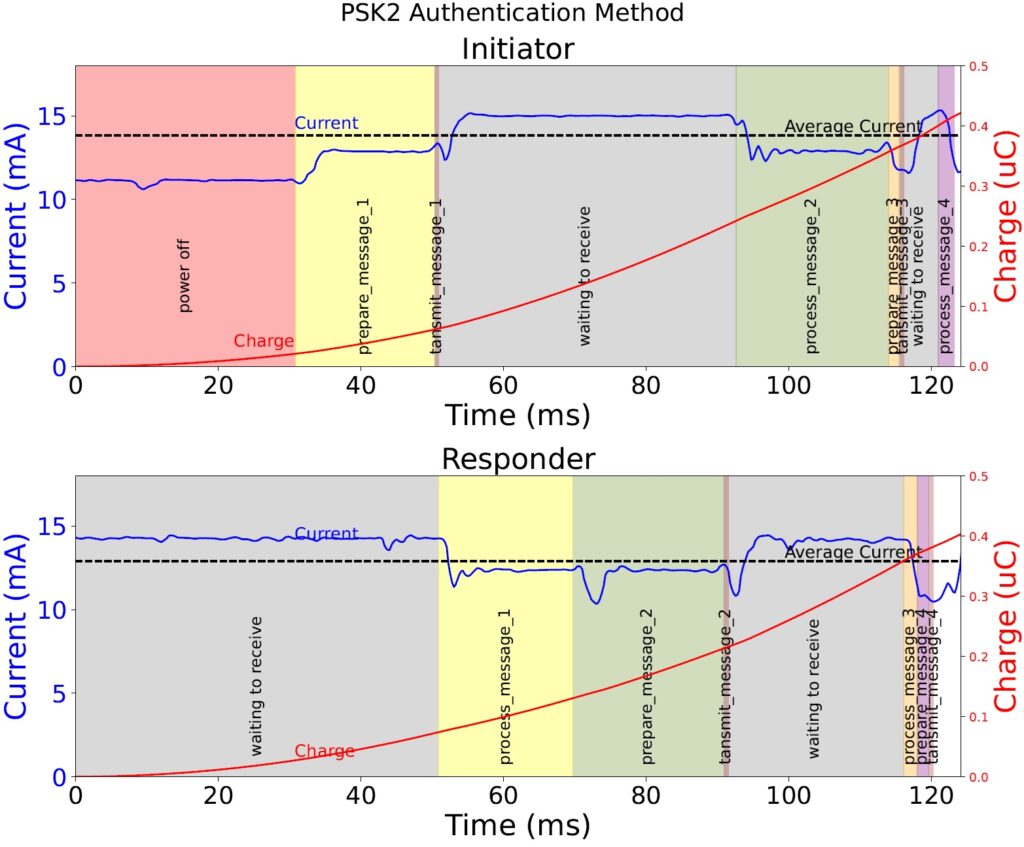
The rapid growth of the Internet of Things ecosystem has intensified the need for secure, resource-efficient communication protocols. The EDHOC protocol is a lightweight authenticated keyexchange protocol, recently developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force. EDHOC addresses the challenges of transport over constrained radio technologies and execution on constrained microcontroller units. In its standardized version, the key-exchange can be authenticated using signatures or static Diffie-Hellman keys. However, many Internet of Things deployments in the wild rely on Pre-Shared Keys. As such, the potential use of EDHOC in those deployments requires a new authentication method for this protocol, based on Pre-Shared Keys. Two variants of Pre-Shared Keys authentication in EDHOC are currently under consideration in the Internet Engineering Task Force LAKE working group. This paper presents a comprehensive analysis of these variants, examining their performance metrics, implementation complexity, and security and privacy considerations. Our evaluation focuses on computational time, memory usage, and deployment challenges in diverse Internet of Things ecosystems. Based on our analysis, we have formulated a recommendation to the Working Group, which has opted to adopt and standardize PSK2.