Hybrid Multiverse-based Parallel Computing Framework for Task Scheduling in Swarm Robotics,
Mohmmadsadegh Mokhtari, David Scalais, Jeroen Famaey, presented at the
IEEE Computing, Communications and IoT Applications Conference (ComComAp), https://comcomap.net/2025/program-details.php
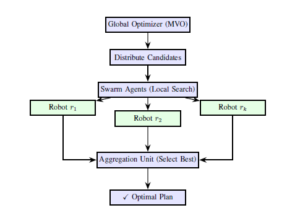
Abstract: Energy-aware task scheduling in large robotic swarms is challenging due to computational complexity, communication overhead, and limited onboard energy. Traditional centralized schedulers struggle to scale, while fully distributed approaches often lack global coordination. To address this, we propose a hybrid scheduling framework in which a central coordinator performs global task allocation using a Multi- Verse Optimizer (MVO), and the swarm itself participates in parallel local schedule refinement. After receiving their assigned task subsets, individual robots refine execution order using Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) or Genetic Algorithms (GA), allowing computation to be distributed across the swarm rather than concentrated at the center. This significantly reduces central processing demand by offloading while adapting task execution to local energy conditions. The framework is implemented in a ROS–Docker environment with explicit energy-aware scheduling. Experimental results show that the approach reduces scheduling computation time by up to 250% and lowers mission makespan by 5–7% compared to six state-of-the-art methods, while improving overall energy efficiency and coordination. These findings demonstrate that combining centralized global insight with distributed parallel refinement enables scalable and energy-efficient swarm task scheduling suitable for large-scale deployments.